Carbon Filtration
Water Purification to Remove CTO and VOCs
What is the Purpose of a Carbon Filter?
Removal of CTO
Eliminates chlorine, unpleasant tastes, and odors from water.
Removal of VOCs
Removes volatile organic compounds, including pesticides.
Enhances Taste & Smell
Significantly improves the taste and smell of water.
Charcoal, which is produced by burning bamboo or husks, primarily consists of pure carbon. When used as a filter, this carbon (or charcoal) filter serves as a natural medium to remove chlorine, taste, odor (CTO), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as pesticides. It also enhances the taste and smell of water—a crucial benefit in Singapore, where chlorine is often added to water by the Public Utilities Board (PUB).
What is Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) Filtration?
Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) is produced by heating organic materials like coal, wood, or coconut shell in the absence of air, then crushing them into granules. This material is a highly porous adsorbent, making it exceptionally effective at reducing taste, odor, and chlorine in water. Such capabilities are vital because chlorine and chloramines used by water treatment plants can create carcinogenic by-products that linger in drinking water, giving it an artificial, chemical taste.
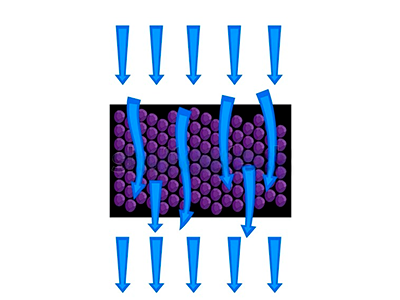
This filtration capability works as follows: when water flows through the cartridge and contacts the carbon filter, the positively charged GAC attracts negative ions such as ozone, chlorine, fluorides, and dissolved organic solutes from the water. The loose granules of activated carbon allow water to pass through easily, while contaminants adhere to the surface of the carbon filter.
Despite its effectiveness, there are three main issues associated with GAC filters: channeling, dumping, and a relatively large pore size. However, these problems are related to the design of the filters and the use of loose carbon granules, not the activated carbon media itself.
What is a Carbon Filter?
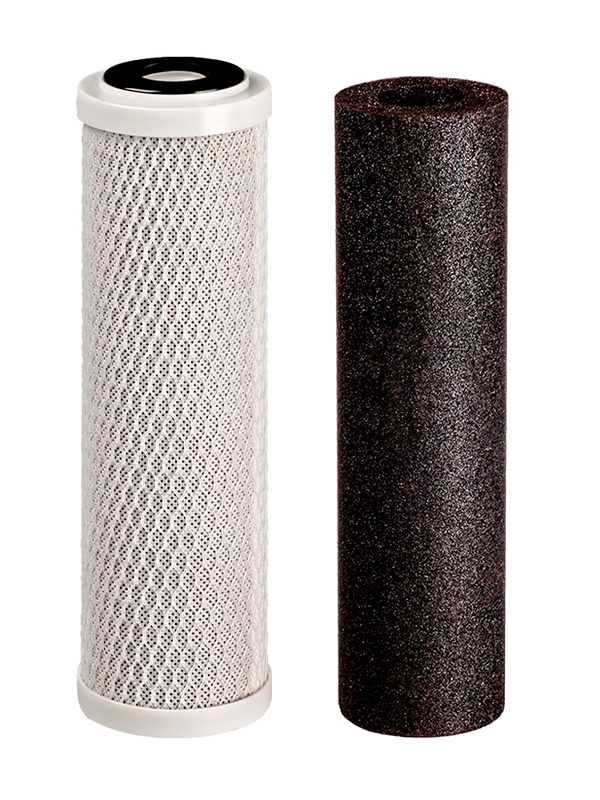

The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends using carbon filters to remove chlorine, taste, odor (CTO), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as pesticides from water.
These carbon filters can be made from coal, wood, nut shells, or bamboo. The use of carbon as a water purifier dates back to ancient Egyptian times, where it was recognized for its powerful absorbent properties, which effectively trap contaminants during water filtration.
In recent years, coconut shell carbon has become the preferred material for manufacturing carbon filters in the industry. The reason is simple: coconut shell is a renewable resource, and 85-90% of its surface area consists of micro-pores. These micro-pores effectively trap a higher number of contaminants. For easier understanding, think of the micro-pores in the carbon filter as parking spaces where contaminants are captured as water flows through.
What is an Activated Carbon Filter?
Activated carbon used in filters undergoes additional processing to further open the pores, increasing the surface area and giving the filter greater capacity to trap contaminants.
Types of Activated Carbon Filters
Activated carbon filters are generally categorized by micron size, preparation method, and industrial application. The three most common types of activated carbon filters used in water filtration are:
⦁ Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) Filter: Composed of individual carbon granules, GAC filters provide an easy channel for filtration. They are typically chosen for their cost-effectiveness, maintaining good water flow and pressure without compromising filtration quality.
⦁ Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC): Made from finely ground activated carbon, PAC particles are used in carbon block filters. With much finer granules than GAC, PAC has a larger surface area, making it more effective at filtration. However, this results in lower water flow and pressure, requiring more frequent filter changes.
⦁ Impregnated Carbon: These carbon particles are infused with inorganic compounds like silver, which inhibit microbial growth. Silver-loaded activated carbon is often used as an adsorbent in water purification due to its antimicrobial and antiseptic properties. However, this is not commonly used in Singapore because the water is already disinfected with chlorine.
How Often Should I Replace the Activated Carbon Filter?
Puriwell Global recommends replacing a single 10” GAC Activated Carbon filter after a maximum of 12 months. The reason is straightforward: once the Activated Carbon Filter is saturated and can no longer trap chlorine and other contaminants, it must be replaced to maintain its effectiveness.
